What is Polycystic ovarian syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder among the women at the age of reproduction. Women with PCOS have excess androgen levels (male hormones), infrequent or missed menstrual periods. The ovaries may develop numerous small collections of follicles (fluid) and fail to release or produce the egg regularly that causes infertility. The root cause of the polycystic ovarian syndrome is not known. Early diagnosis of polycystic ovarian syndrome and its treatment, along with weight loss, can lessen the risk of long-term issues such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
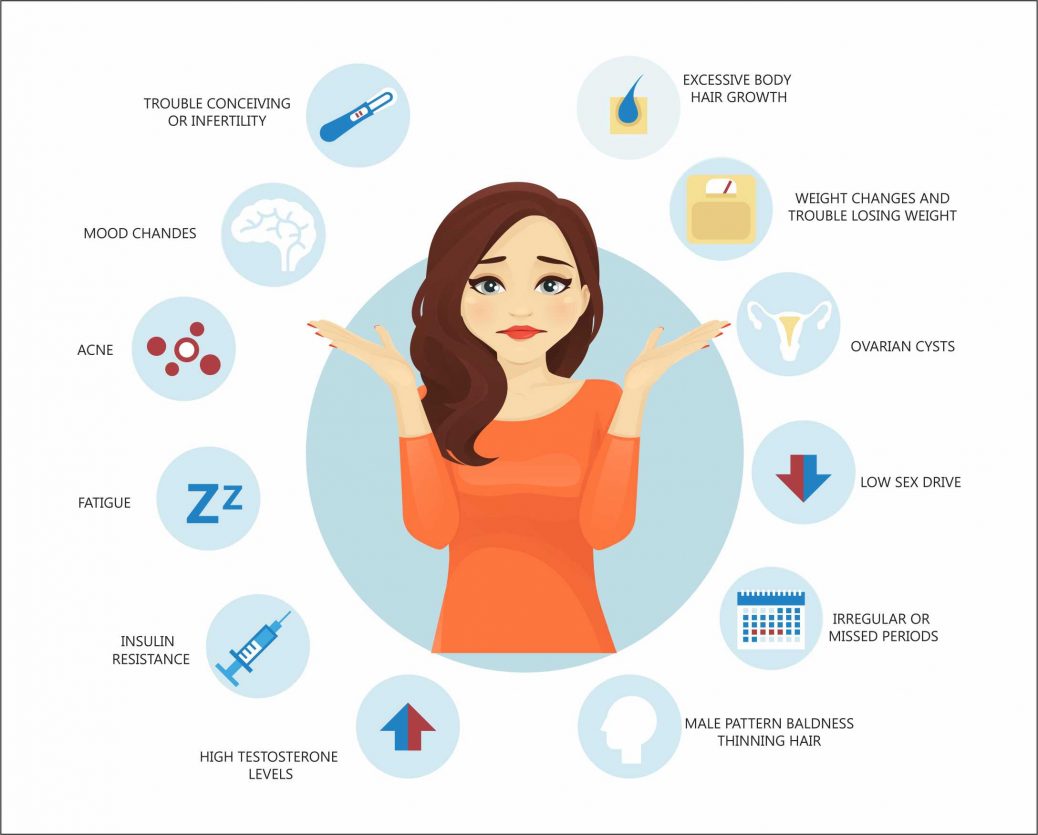
What Signs and Symptoms does Polycystic ovarian syndrome have?
The signs and symptoms of PCOS appear around the same time as the first period, or if the mensuration cycle is consistently irregular (sporadic, absent) 2–3 years after menarche. But in some cases, the development of PCOS happens later, for example, because of substantial weight gain. The signs and symptoms of PCOS vary from person to person. The polycystic ovarian syndrome is diagnosed when you experience at least two of the below-mentioned signs and symptoms:
- Irregular periods: Missed, irregular, or prolonged menstrual cycles are the most common sign of PCOS. For example, you can have less than nine periods a year, more than 35 days between the 1-period cycle and abnormally heavy periods.
- High level of androgen (male hormones): High levels of male hormone might result in physical signs and symptoms of the polycystic ovarian syndrome. For example, excess facial and body hair (hirsutism), and abnormally severe acne issues and male-pattern bald-headedness.
- Polycystic ovaries: The ovaries of women with Polycystic ovarian syndrome might be enlarged and contain follicles (fluid) that surround the eggs. As a consequence, the ovaries might fail to function normally, which will then result in the regular release or production of the eggs.
- Infertility: PCOS negatively effects fertility as women with the syndrome do not ovulate, or release an egg, each month because of the overproduction of estrogen by the ovaries. As ovulation does not occur regularly, periods cycle becomes irregular and there is an increase in the levels of hormones such as testosterone, that can affect the quality of the egg, obstructive ovulation, lead to insulin resistance, and also increases the risk of other disorders such as gestational diabetes and heart problems.
Signs and symptoms of Polycystic ovarian syndrome are characteristically more severe if you are obese or overweight.
When to see a doctor
See a gynecologistif, you have concerns regarding your regular period, if you are experiencing the issue of infertility or if you have signs and symptoms of a polycystic ovarian syndrome, like excess androgen such as worsening hirsutism, acne, and male-pattern baldness.
Causes of polycystic ovarian syndrome
The root cause of Polycystic ovarian syndrome is not known. Factors that majorly play a role are:
- High level of insulin: Insulin is the hormone released in the pancreas that lets the cells to use sugar. Insulin is the primary energy supplier of your body. If your cells become unaffected to the action of insulin, then your blood sugar levels can increase, and your body might produce excess insulin. A high level of insulin can increase the production of the androgen, causing difficulty in the procedure of ovulation.
- Low-grade inflammation: The term low-grade inflammation is used to define the production of white blood cells tofight infection. Research shows that women with the signs and symptoms of thepolycystic ovarian syndrome has a type of low-grade inflammation thatstimulates the polycystic ovaries to produce more androgens, which can causeproblems related to heart and blood vessels.
- Heredity: Certain genes might be allied to PCOS.
- High level of male hormones: The ovaries produce unusually high levels of androgen (male hormones), which results in hirsutism and acne.
Complications caused by the signs and symptoms of the polycystic ovarian syndrome include:
- Infertility
- Pregnancy or diabetes: Encouraged because of high blood pressure
- Miscarriage or premature birth of the baby
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A severe inflammation in the liver caused because of the excessive accumulation of the fat in the liver.
- Pre-diabetes or type 2 diabetes
- Sleep apnea
- Eating disorders, depression, and anxiety issues
- Abnormal bleeding
- Endometrial cancer (cancer of the uterine lining)
- Metabolic syndrome: A cluster of complication including high blood pressure, high level of blood sugar, and nonstandard cholesterol or triglyceride levels that increase the risk of cardiovascular disease
Lifestyle changes
After the right diagnosis of the signs and symptoms of polycystic ovarian syndrome at right time, your doctor can suggest you lose weight through a low-calorie diet with regular exercise activities. For example, losing 5% of your body weight — can reduce the problems of ovulation and other symptoms of PCOS. Losing weight can also upsurge the effect of medications that your doctor recommends for PCOS, and can also help you to deal with infertility.
PCOS symptoms and treatment generally twitches with lifestyle variations like losing weight, control on a diet, and workout.
- Losing just 5% to 10% of your body weight can help control your menstrual cycle and recover the signs and symptoms of the polycystic ovarian syndrome. Losing weight can also improve cholesterol stages, lessen insulin, and reduce heart disease and diabetes menaces.
- Following a diet chart can help you lose weight. Though, some foods may have compensations over others.
- Low-carbohydrate meals are useful for both losing weight and redesigning insulin levels. A low glycemic index (low-GI) meal that has the most carbohydrates from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains benefits in regulating the menstrual cycle recovering than a regular weight loss meal.
- A few researchers have found that moderate-intensity exercise of at least 30 minutes for a minimum of three days a week can benefitwoman with PCOS to lose weight. Losing weight with workout also progresses ovulation and the level of insulin in the body.
- The workout is even more beneficial done with a healthy and controlled diet. Diet plus exercise helps you lose more weight than either intrusion alone, and it lessens the risk of diabetes and heart disease.
The signs and symptoms of polycystic ovarian syndrome highlights dealing with your concerns, such as infertility, hirsutism, acne, or obesity. Precise symptoms and treatment might require different changes, like lifestyle changes or medication.
Medications:
To regulate the signs and symptoms, your doctor might recommend:
- Combination birth control pills: Pills that comprise of the estrogen and progestin reduces the production level of the androgen (male hormones) and control estrogen. Hormones regulation can lower the danger of endometrial cancer, and cure the issue of abnormal bleeding, excessive hair growth and severe acne problems. Instead of pills, you can also use a skin patch or vaginal ring that comprises a blend of estrogen and progestin.