Hirsutism in Polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal syndrome that affects 10% –15% of women. because of the inconstant nature of PCOS, its diagnosis is grounded based on the blend of clinical, ultrasound, and laboratory aspects.
Polycystic ovary syndrome is an ailment linked with hormonal imbalances that cause the ovaries to overproduce androgens. Hirsutism in PCOS is a common problem. In women with PCOS, several minor follicles grow in the ovaries that look like cysts, hence the term “polycystic.” These minor cysts are juvenile ovarian follicles that failed to develop and ovulate.
Why hirsutism occurs in women with PCOS?
Hirsutism is a manifestation of excessive male hormones in the blood which is called hyperandrogenemia or in the local skin areas which are called hyperandrogenism. So, for example, if you see the blood test of a women with PCOS her blood reports will not show excess androgens at all, because the androgens may not be present in the blood but the androgens might be present in the local areas of the skin, where there are certain enzymes like the 5-Alpha reductase type-2 enzyme which converts testosterone to an extremely active form which is called dihydrotestosterone and that tends to stimulate the excessive hair growth.
The androgens are influenced by insulin. And there is a link between hyperinsulinemia which is the hormone and modulates the blood sugar in the body. Hyperinsulinemia is one of the main manifestations of Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). And it is linked to the androgens in the body and causes the levels of free testosterone to rise in blood and also increase the conversion of testosterone to the active form in the skin. That is why hirsutism in PCOS is caused by the increased action of the male hormones.
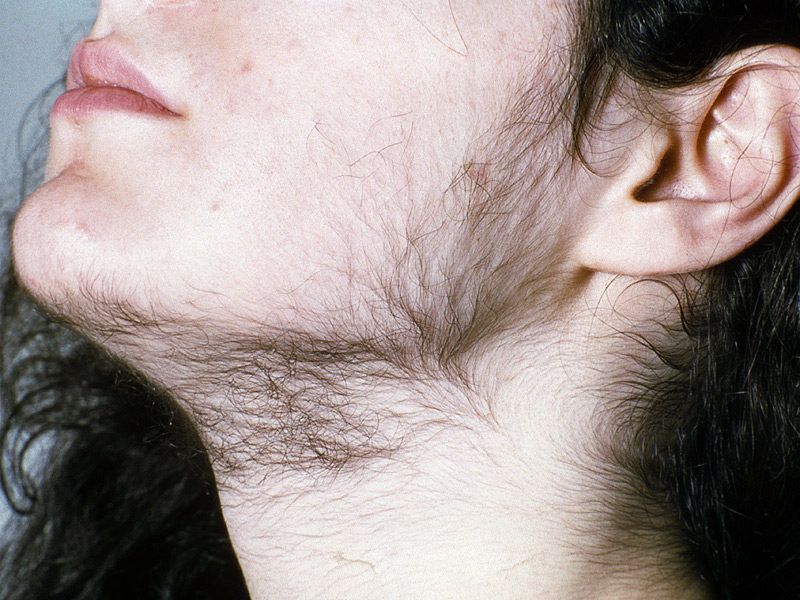
Hirsutism in PCOS is the extreme growth of hair on the body and face of women with PCOS. Hirsutism can be seen as abrasive, dark hair that can appear on the chest, abdomen, face, back, upper arms, upper lips. Hirsutism is an indication of medical ailments linked with the male hormones which are known as androgens. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), in which the ovaries excessively produce androgens, and that is the root cause of hirsutism in PCOS and can affect up to 15% of women. Hirsutism in PCOS is very communal and often recovers with medical supervision. Speedy medical care is significant because adjourning treatment can complicate the treatment procedure and may have long-term health problems.
Outline of normal hair growth
Knowing the process of normal hair growth will help you comprehend hirsutism in PCOS. Each hair grows from a follicle profound in your skin. As long as these hair follicles are not entirely devastated, the hair will endure growing even if the channel, which is the fragment of the hair that looks above the skin, is pulled or detached. Hair follicles protect all the parts of your body excluding the underside of your feet and the palms of your hands. Out of the approximately 50 million hair follicles causing your body, one fifth is positioned on your scalp. The number of hair follicles you have never increase after birth but gradually instigates to decrease by the age of 40.
Hair thickness differs from the traditional origin. Men and women of a similar ethnic cluster have identical figures of hair follicles and identical hair patterns. Excessive hair that is due to heredity or ethnic discrepancy rather than hormonal reasons is characteristically sited on the hands, legs, and feet, while hirsutism in PCOS typically affects the face, abdomen area, chest, upper lips inner thighs, and back. Hair growth occurs in cycles. Hormonal changes associated with oral contraceptives (birth control pills) or pregnancy, may synchronize the growth of the hair and make it appear to grow and shed more than usual.
Effects Of Androgens On Hair Growth
Hirsutism in PCOS results with excess hair on the body and face is usually because of the excessive presence of androgens in your body. Androgens are present in both women and men, but men have much higher echelons of purely active androgens. In men, androgens are released mainly by the testes and the adrenal glands. In women, androgens are released by the ovaries and the adrenal glands. To some extent, estrogen decreases the result of androgens in women. If your hair follicles are hormone-sensitive, androgens may cause some vellus hairs to change to deadly hairs and cause the dead hairs to grow faster and thicker. Androgens increase sebum production, which consequences in oily skin and acne problems. Excess androgens can reason irregular menstruation or absent ovulation. The effects of excess androgens are known as virilization, happen infrequently, and generally seen in a woman with PCOS.
Androgen-sensitive sites of hair growth in women with Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Upper lip, Chest, and sternum
- Inner thighs
- Lower abdomen
- Breasts Upper back
- Beard area Upper abdomen
- Lower back
Identifying Hirsutism
In the primary medical consultation, your doctor will try first to make out the difference between deadly hairs budding in a male pattern signifying hirsutism in PCOS and hair growth because of genetic or ethnic tendencies. If you are diagnosed with hirsutism, you should get a blood test, ultrasound and hormone tests done to assess the proper functioning of your ovaries and adrenal glands. After classifying the reasons for hirsutism, you should get proper treatment from the doctor.
CAUSES OF HIRSUTISM IN PCOS
- Excessive release of androgens by the ovaries (polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), tumor)
- Excessive release of androgens by the adrenal glands (nonclassical-adrenal-hyperplasia)
- Insulin resistance
- Hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance, acanthosis nigricans (HAIR-AN disorder)
- Excessive release of cortisol by the adrenal glands (Cushing syndrome)
- Menopause
- Medicines
What are the treatment options available to treat hirsutism in PCOS?
Hirsutism in PCOS you can see excess hair growth all over the body and face. So, the standard hair removal techniques which are used by the normal woman without PCOS can be used by a woman with PCOS as well as waxing, threading, bleaching, plucking or depilation and contemporarily laser hair removal treatment. But these techniques would not aid in preventing the growth of the hair, these techniques would just remove the excess hair but not prevent the growth which is the major problem in a woman with PCOS.
Laser hair removal treatment, which is commonly used today is expensive but has one advantage because it is permanent hair reduction treatment. When you use the technique of laser hair removal treatment or light technology to remove hair, it causes miniaturization of the hair which means your dark and thick hair will become finer and thinner and will reduce hirsutism in PCOS over some time. If you compare the other standard treatment of hair removal vs laser hair removal treatment, the standard treatments would take years to reduce the thickness and texture whereas laser hair removal treatment would do that in 6 to 8 treatments. And laser hair removal treatment tends to cause permanent hair reduction, because of the miniaturization the courser hair tends to become finer and thinner throughout the time. Also, a woman with Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) has a hormonal imbalance because of which the hair will come back. So, the laser hair removal treatment should be considered as a hair removal technique and not something that will allow a woman with PCOS to get rid of their internal hormonal problem which is causing hair growth. With laser hair removal treatment there is a definite clean period where a woman with PCOS is hair free and there is a delay in re-growth of the hair. In today’s times if a woman with Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can afford it then the laser hair removal can be done with an Nd YAG laser or a Diode laser or even intense pulsed light are the various modalities to reduce hair.