Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Symptoms
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a common condition prevailing in women of reproductive age. PCOS can develop any time after a woman has had her first period (known as menarche). There are numerous instances where PCOS development can occur in later reproductive years as a response to certain hormonal factors. PCOS has various signs and symptoms-one felt by the patient, and one deduced by the doctor on thorough examination and medical counseling.
In order to reach a definitive diagnosis of PCOS, your doctor will observe for at least one of these two symptoms.
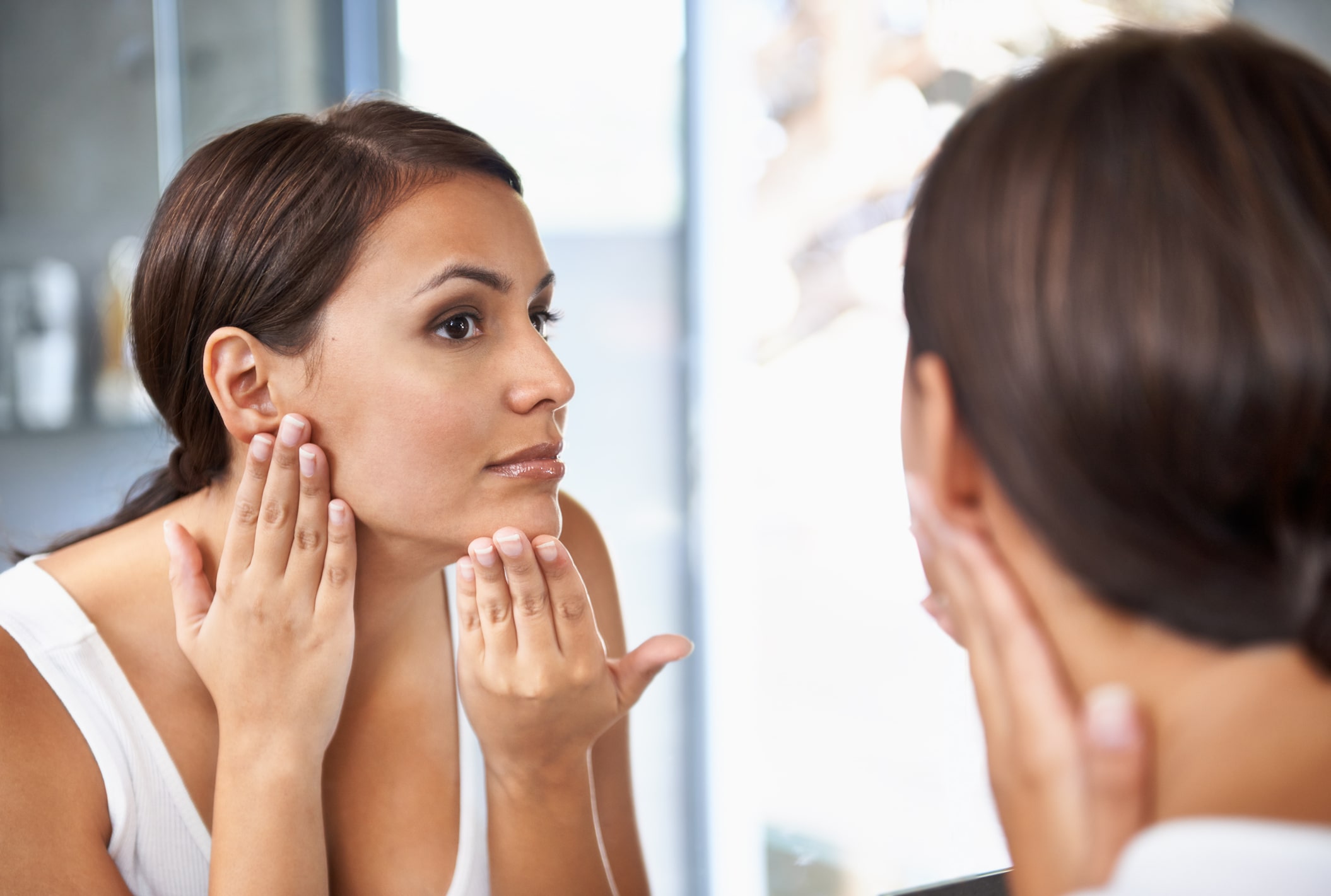

Irregular periods
This is the most commonly encountered symptom. The outcomes include menstrual intervals (time gap between two sequential periods) exceeding 30 days, four or more non-menstruating months, extended periods of more than eight days, with heavy or scant bleeding.
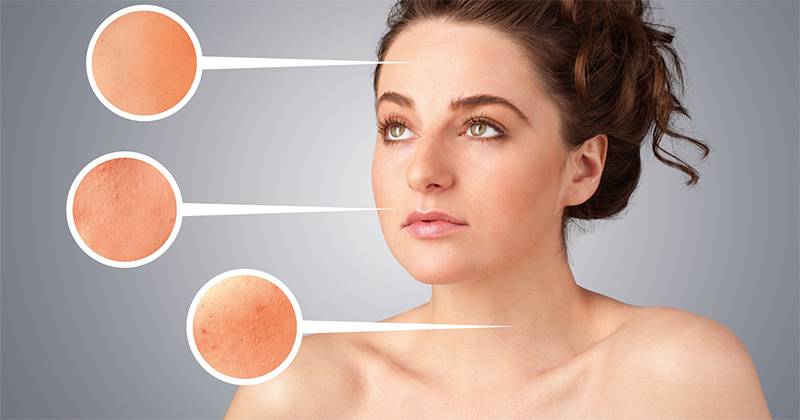
Excess androgen
- Another hallmark symptom of PCOS is excess secretion of the male hormone, androgen. This manifests in visible physical signs such as excess facial and body hair (hirsutism), adult or severe adolescent acne, and male pattern baldness, thinning of hair and excess hair on fingers of hands and toes, and on the surface of hands and legs.
- When observed under ultrasonography or any other imaging technique, polycystic ovaries are abnormally larger in size as compared with that of the normal ones and contain fluid-filled sacs that surround the eggs.
Other symptoms of PCOS include
- acne
- weight gain
- anxiety or depression
- infertility
People with PCOS often have co-existing chronic disorders such as diabetes, hypertension and high cholesterol, which should not be confounded as symptoms. These conditions lead to increased weight gain in PCOS patients.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Symptoms Pain
PCOS is often accompanied by pain. “As the syndrome is caused by immature eggs which grow on the ovaries and later lead to the hormonal imbalance. This hormonal imbalance can make Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Symptoms painful, causing cramping and bloating,”
Polycystic ovarian syndrome symptoms pain is one of the common problems in women. However, the PCOS Pain in the ovary could be because of ovulation or because of a cyst. The polycystic ovarian syndrome symptoms pain is transient and heals with time.

PCOS Symptoms and Treatment
The PCOS symptoms and treatment varies from patient to patient, and the medication is highly individualistic. Along with medication, lifestyle modification strategies such as physical exercise and a healthy diet prove to be of equal benefit and significance as that of medications for the PCOS symptoms and treatment.
Lifestyle changes
PCOS is highly associated with obesity (excess fat tissue in the body). Hence, as a lifestyle modification strategy, the doctor will first recommend losing weight by resorting to physical exercise and diet. The effectiveness of PCOS medications also tends to improve with reduced weight.
As aforementioned, a low-fat diet is associated with significant improvements leading to the alleviation of symptoms of PCOS. A typically recommended weight loss amounts to a reduction of 5% of your body weight, for example: If your weight is say 60 kg, you need to lose your weight by at least 3 kg to start with.